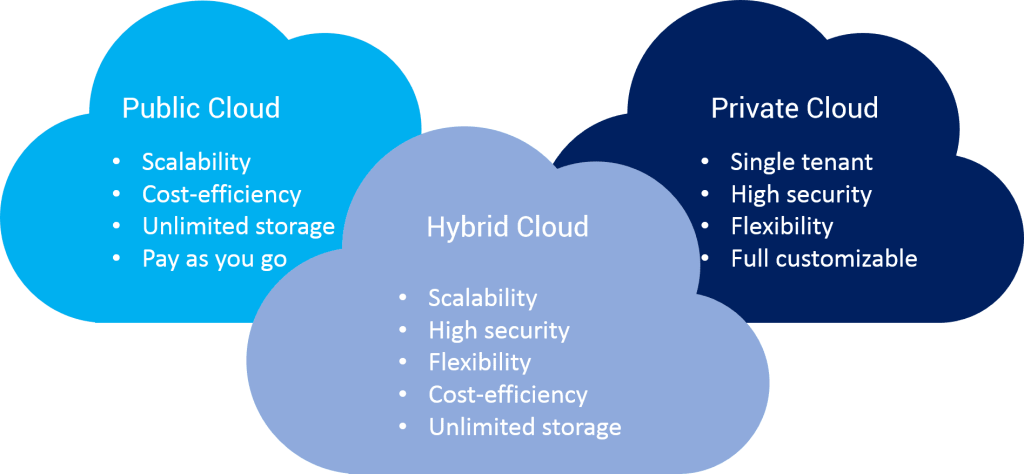
In today’s digital age, cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer for businesses seeking flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in managing their IT infrastructure and applications. One of the fundamental decisions organizations face when adopting cloud technology is choosing the right deployment model. In this article, we’ll explore the three primary types of cloud solutions: public, private, and hybrid clouds, highlighting their unique characteristics, advantages, and use cases.
Public Cloud
Public cloud solutions are infrastructure and services provided by third-party cloud service providers on a pay-as-you-go basis over the internet. These solutions are hosted and managed by cloud providers, who offer a range of services, including computing power, storage, networking, and software applications, to multiple customers simultaneously.
Characteristics of Public Cloud:
- Shared infrastructure: Resources are shared among multiple users, allowing for cost savings and scalability.
- Accessibility: Accessible over the internet from anywhere, making it ideal for remote work and collaboration.
- Scalability: Resources can be scaled up or down dynamically based on demand, enabling businesses to accommodate fluctuations in workload.
- Cost-effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go pricing model eliminates the need for upfront capital investment and allows businesses to pay only for the resources they use.
Advantages of Public Cloud:
- Cost Savings: Eliminates the need for purchasing and maintaining on-premises hardware and software, reducing capital and operational expenses.
- Scalability: Offers unlimited scalability, allowing businesses to easily scale resources up or down in response to changing demand.
- Accessibility: Provides ubiquitous access to resources and applications over the internet, enabling seamless collaboration and remote work.
Use Cases for Public Cloud:
- Development and Testing: Provides on-demand access to computing resources for software development, testing, and deployment.
- Web Hosting: Hosts websites, web applications, and e-commerce platforms, ensuring high availability and scalability.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for on-premises installation and maintenance.
Seek guidance from a Microsoft Partner for expert advice on making informed decisions about adopting cloud technology
Private Cloud
Private cloud solutions are dedicated cloud environments deployed and managed for a single organization, either on-premises or in a third-party data center. Unlike public clouds, private clouds offer exclusive access to computing resources and greater control over security, compliance, and customization.
Characteristics of Private Cloud:
- Dedicated Infrastructure: Resources are dedicated to a single organization, providing enhanced security and control.
- Customization: Allows organizations to tailor the cloud environment to their specific requirements, including hardware, software, and security policies.
- Security and Compliance: Offers greater control over data security and regulatory compliance, making it suitable for industries with strict compliance requirements.
- Performance: Provides predictable performance and low-latency connectivity, ideal for mission-critical applications and sensitive workloads.
Advantages of Private Cloud:
- Enhanced Security: Offers greater control over data security and privacy, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and protecting sensitive information.
- Customization: Enables organizations to customize the cloud environment to meet their specific business needs, optimizing performance and efficiency.
- Predictable Performance: Provides consistent performance and reliability, making it suitable for high-performance computing and critical workloads.
Use Cases for Private Cloud:
- Highly Regulated Industries: Ideal for industries such as healthcare, finance, and government, which have strict data security and compliance requirements.
- Mission-Critical Applications: Supports applications that require high availability, reliability, and performance, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and database management.
- Confidential Data Processing: Used for processing and storing sensitive information, such as intellectual property, proprietary data, and customer records.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud solutions combine the features and capabilities of both public and private clouds, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of each deployment model while addressing specific business requirements and workload demands. In a hybrid cloud environment, workloads can be dynamically distributed between public and private cloud resources based on factors such as performance, security, and cost.
Characteristics of Hybrid Cloud:
- Integration: Provides seamless integration and interoperability between public and private cloud environments, enabling workload portability and data mobility.
- Flexibility: Offers flexibility to deploy workloads in the most appropriate cloud environment based on factors such as performance, security, and compliance requirements.
- Scalability: Allows organizations to scale resources up or down dynamically across public and private clouds to accommodate changing workload demands.
- Cost Optimization: Optimizes costs by allocating workloads to the most cost-effective cloud environment while ensuring performance and reliability.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud:
- Flexibility: Offers flexibility and agility to meet changing business needs, enabling organizations to leverage the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public clouds while maintaining control over sensitive workloads in private clouds.
- Scalability: Provides unlimited scalability by extending on-premises infrastructure to public cloud resources during peak demand periods, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization.
- Security: Enhances security by allowing organizations to keep sensitive data and workloads in private clouds while leveraging the security controls and compliance certifications of public cloud providers.
Use Cases for Hybrid Cloud:
- Bursting Workloads: Allows organizations to offload peak workloads to the public cloud during periods of high demand, ensuring optimal performance and scalability without overprovisioning on-premises infrastructure.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Facilitates data replication and backup between on-premises and public cloud environments, ensuring data resilience and business continuity in the event of a disaster.
- Regulatory Compliance: Enables organizations to maintain compliance with regulatory requirements by keeping sensitive workloads and data in private clouds while leveraging the cost-effective and scalable resources of public clouds for non-sensitive workloads.
Conclusion
In conclusion, public, private, and hybrid cloud solutions offer organizations a range of options for deploying and managing their IT infrastructure and applications. Each deployment model has its own unique characteristics, advantages, and use cases, allowing businesses to choose the solution that best meets their specific requirements and objectives. Whether it’s maximizing cost savings and scalability with public clouds, enhancing security and compliance with private clouds, or leveraging the flexibility and agility of hybrid clouds, organizations can benefit from the diverse capabilities of cloud solutions in today’s digital economy.